Manage Tenant Control Planes with GitOps
This guide describe a declarative way to deploy Kubernetes add-ons across multiple Tenant Clusters, the GitOps-way. An admin may need to apply a specific workload into Tenant Clusters and ensure is constantly reconciled, no matter what the tenants will do in their clusters. Examples include installing monitoring agents, ensuring specific policies, installing infrastructure operators like Cert Manager and so on.
This way the tenant resources can be ensured from a single pane of glass, from the Management Cluster.
Flux as the GitOps operator
As GitOps ensures a constant reconciliation to a Git-versioned desired state, Flux can satisfy the requirement of those scenarios. In particular, the controllers that reconcile resources support communicating to external clusters.
In this scenario the Flux toolkit would run in the Management Cluster, with reconcile controllers reconciling resources into Tenant Clusters.
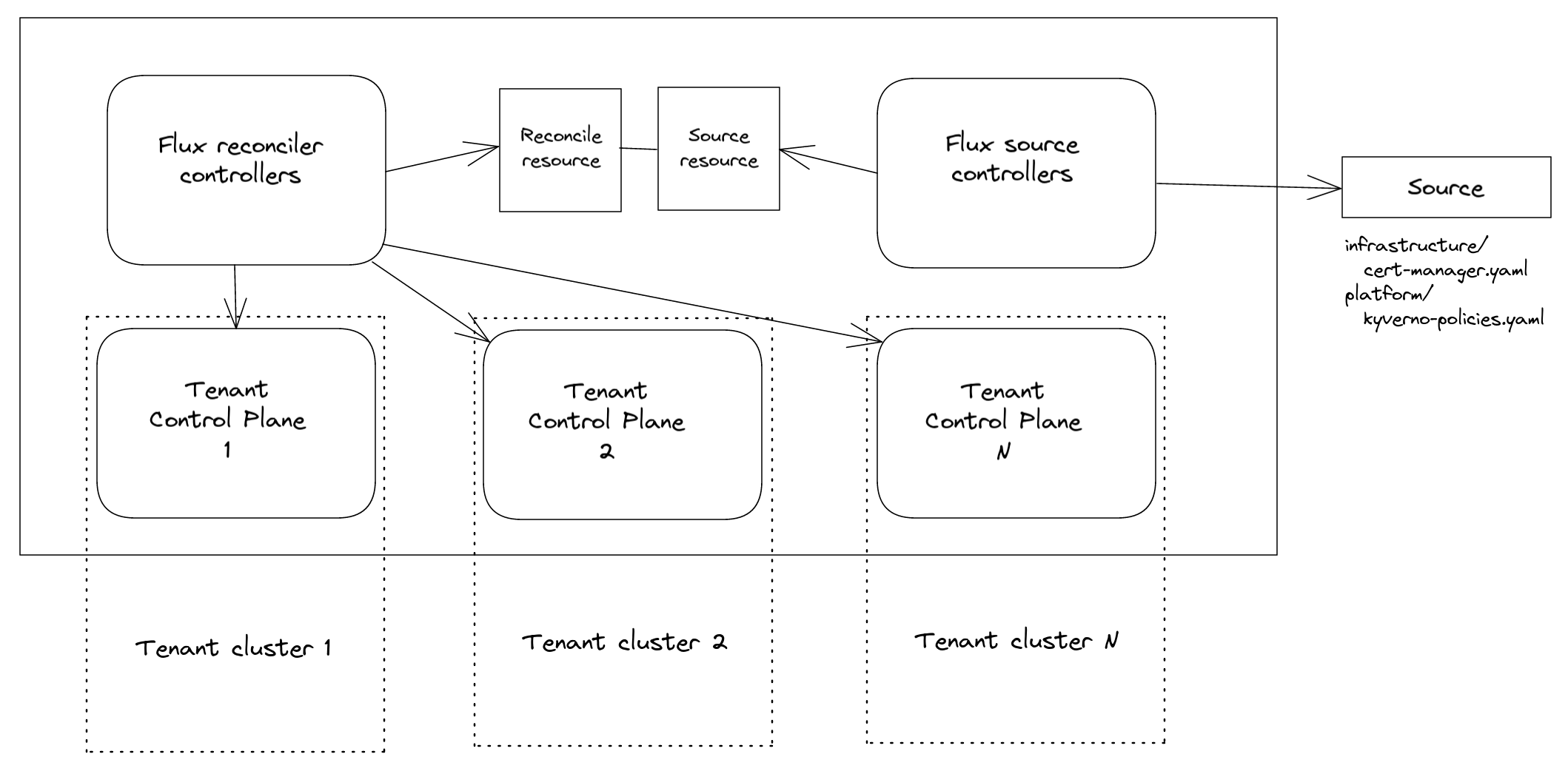
This is something possible as the Flux reconciliation Custom Resources specifications provide ability to specify Secret which contain a kubeconfig - here you can find the related documentation for both Kustomization and HelmRelease CRs.
Quickstart
Once a TenantControlPlane is deployed, the kubeconfig for the admin user can be found in a Secret named as Namespace where the resource has been created.
Let's suppose a TenantControlPlane named tenant1 has been deployed in the tenants Namespace, a Secret named tenant1-admin-kubeconfig is created in the tenants Namespace.
$ kubectl get tenantcontrolplanes.kamaji.clastix.io -n tenants
NAME VERSION STATUS CONTROL-PLANE-ENDPOINT KUBECONFIG AGE
tenant1 v1.25.1 Ready 172.18.0.2:31443 tenant1-admin-kubeconfig 108s
As the admin user has cluster-admin
ClusterRoleit will have the necessary privileges to operate on Custom Resources too.
Given that Flux it's installed in the Management Cluster - guide here - resources can be ensured for specifics Tenant Clusters, by filling the spec.kubeConfig field of the Flux reconciliation resource.
For example, it might be needed to ensure cert-manager is installed into a tenant1 cluster with Helm. It can be done by declaring an HelmRelease as follows:
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: jetstack
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 1m
url: https://charts.jetstack.io
---
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: tenant1-cert-manager
namespace: tenants
spec:
interval: 5m
kubeConfig:
secretRef:
name: tenant1-admin-kubeconfig
key: admin.conf
targetNamespace: default
chart:
spec:
chart: cert-manager
version: v1.10.1
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: jetstack
namespace: flux-system
interval: 1m
values:
replicaCount: 2
and applying it in the Management Cluster, alongside the related jetstack HelmRepository, in the tenants Namespace.
The result would be having Cert Manager installed in the default Namespace of the tenant tenant1's cluster:
$ kubectl get secret -n tenants tenant1-admin-kubeconfig -o=jsonpath='{.data.admin\.conf}' | base64 -d > /tmp/tenant-1.kubeconfig
$ kubectl --kubeconfig /tmp/tenant-1.kubeconfig get deploy -n default
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
tenant1-cert-manager 2/2 2 2 4m3s
tenant1-cert-manager-cainjector 1/1 1 1 4m3s
tenant1-cert-manager-webhook 1/1 1 1 4m3s
No matter what the tenant users will do on the Tenant Cluster, the Flux reconciliation controllers wirunning in the Management Cluster will ensure the desired state declared by the reconciliation resources applied existing in the Management Cluster, will be reconciled in the Tenant Cluster.
Furthermore, this approach does not need to have in each Tenant Cluster nor Flux neither applied the related reconciliation Custom Resorces.